The Obama Administration’s new Race to the Top District (RTT-D) competition, a competitive grant program on top of the more than 100 programs the Department of Education (DOE) already operates, entices cash-strapped school districts with another $400 million to implement the Obama education agenda.
For the past half-century, federal education funding and control have been growing at the expense of state educational autonomy. The last thing our struggling education system needs is for local school districts to become dependent on Washington for education funding, further centralizing school-level policies in the hands of federal bureaucrats.
RTT-D is an offshoot of the original Race to the Top (RTT), the Obama Administration’s $4.35 billion competitive grant program to states carved out of the “stimulus.” The DOE says the new district-level program will “help schools become engines of innovation”:
Race to the Top, launched in 2009, has inspired dramatic education reform nationwide, leading 45 states and the District of Columbia to pursue higher college- and career-ready standards, data-driven decision making, greater support for teachers and leaders, and turnaround interventions in low performing schools. The next phase proposes to build on those principles at the classroom level to support bold, locally directed improvements in learning and teaching that will directly improve student achievement and educator effectiveness.
Concern about the Administration’s push to nationalize the content taught in schools across America through the Common Core State Standards led some states to pass on the original RTT competition. States like Alaska, Texas, and North Dakota have never applied for RTT grants. Under the new district-level competition, the feds will appeal directly to school districts, offering up millions in exchange for adoption of the White House’s preferred policies.
Applicant districts must agree to implement the four core components of RTT (common standards, teacher evaluations, data systems, and the Administration’s school turn-around model), and must secure school board and teacher union buy-in for their application.
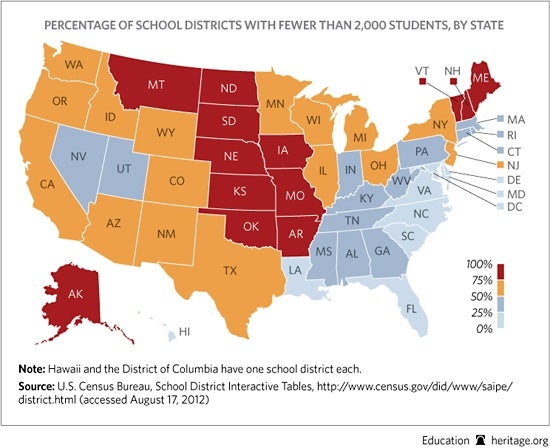
The DOE notes that all school districts with more than 2,000 students are eligible to apply, including those districts in states that did not apply for RTT grants. While smaller school districts may pull together to apply for a grant, the 2,000-student minimum biases larger districts, making it unlikely that small rural school districts will be winners of one of the 15–25 grants that are awarded.
The Administration has demonstrated a pattern of circumventing Congress on key education policy issues. It set an arbitrary deadline for No Child Left Behind reauthorization, and when Congress (in the midst of a thoughtful debate about the future of the nation’s largest education law) failed to meet it, began offering strings-attached waivers to states that agreed to implement the White House’s education agenda. Now the Administration will circumvent states that have chosen not to apply for RTT grants and dangle up to $40 million each to districts willing to toe the line.
It’s another step in centralizing education control and a continuance of Washington-centric education policy that has burdened taxpayers, encumbered states, and failed students for the last half-century.